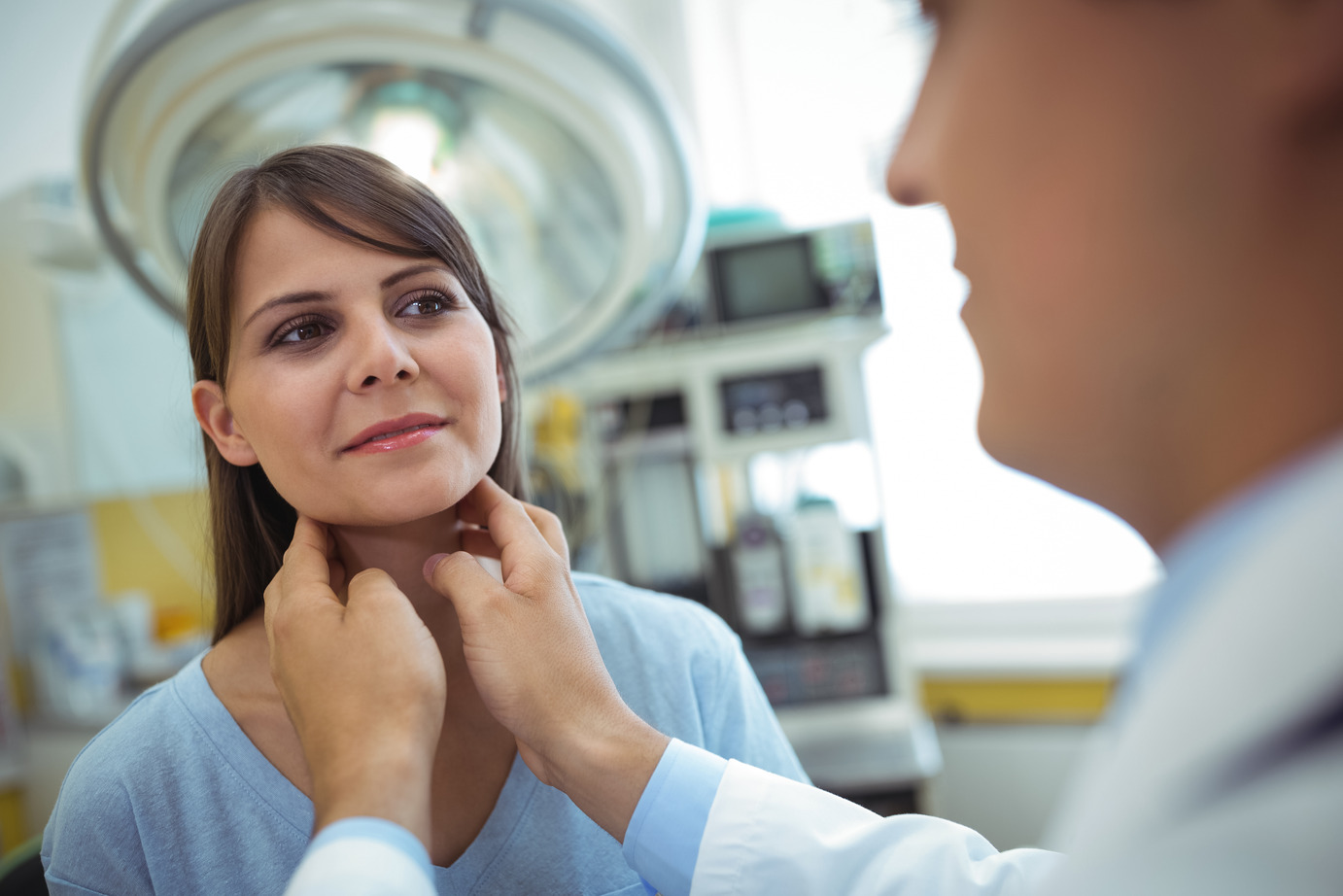
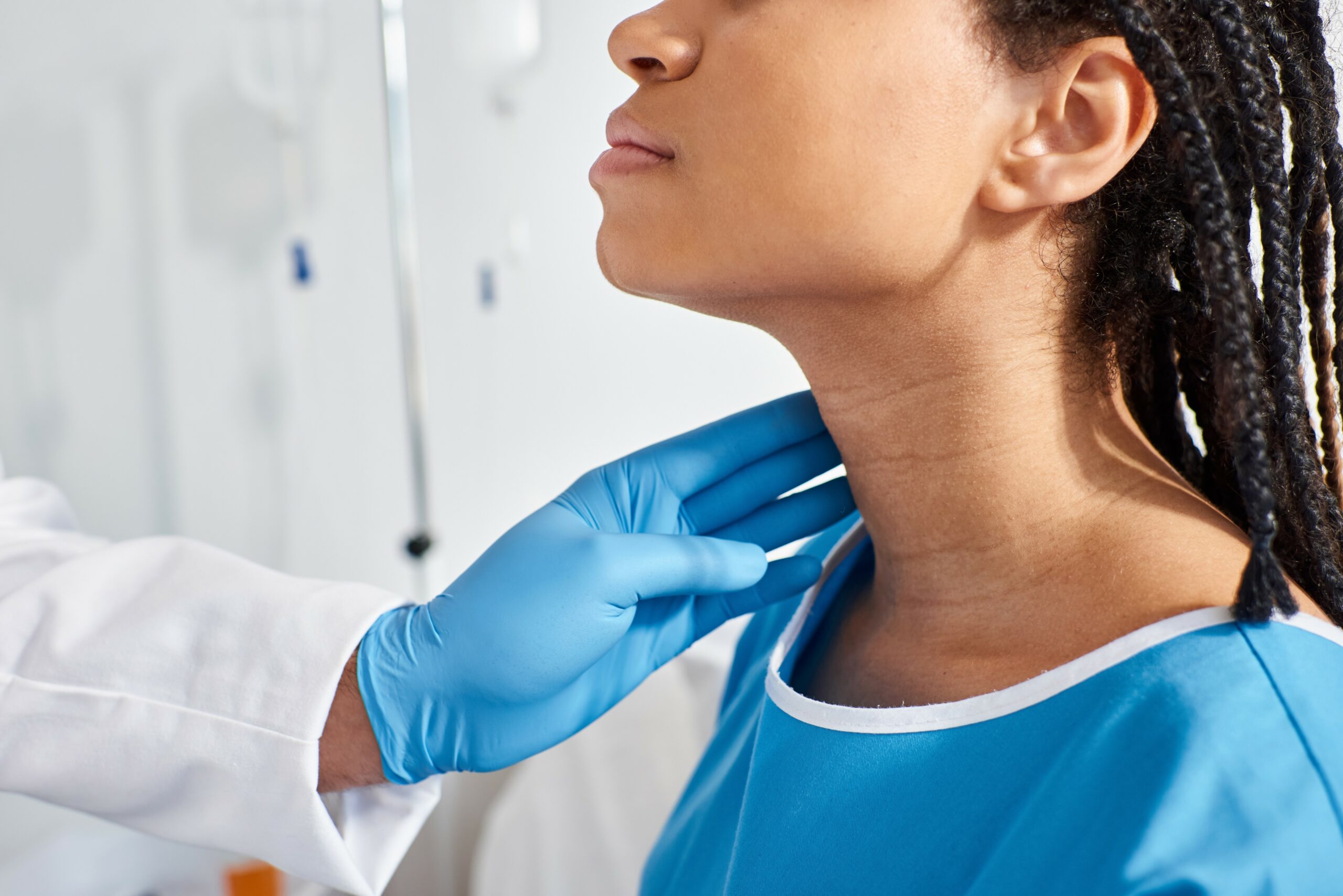
Thyroid ultrasound is a diagnostic imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to create an image of the thyroid. It is a gland located in your neck that secretes hormones that help control heart rate, blood pressure, body temperature, breathing, digestion, and weight. It is used to help identify swelling or enlargement of the gland.
Why Do I Need Ultrasonography?
The ultrasound identifies the cause of swelling or enlargement of the thyroid-gland. The ultrasound can help determine whether the gland enlarges due to a fluid-filled cyst or inflammation. Also, it helps to identify nodules, abnormal masses, and other thyroid-abnormalities. It would be best to visit any of our facilities in tampa, to consult a qualified doctor. Our medical personnel can perform ultrasounds, biopsies, and lab services. Also, we treat complex metabolic conditions like diabetes and obesity. For obesity, we have a comprehensive weight loss program.
Role of Ultrasonography in Thyroid-Disease
The ultrasound works to:
- diagnose and monitor treatment of thyroid-cancer or goiter – makes it possible to detect and manage abnormal growth in the gland (a nodule, tumor, cyst).
- Help diagnose another condition that affects the gland, such as infection or inflammation.
What Are the Risks of an Ultrasound?
No radiation remains in a person’s body from the ultrasound procedure. Risks associated with exposure to high-intensity sound waves during an ultrasound include:
- No radiation remains in a person’s body from an ultrasound exam.
- There are no known long-term risks associated with diagnostic levels of ultrasound.
- Pain, brief discomfort, or mild irritation where the transducer is placed on your neck, if a person has inflamed tissues due to thyroiditis
- Bruising at the site of the ultrasound
Preparing for the Ultrasound
Your endocrinologist will explain the procedure and offer you the chance to ask questions about the possible risks and benefits.
You should let them know if you:
- have a pacemaker or any other implanted medical devices
- have concerns about anesthesia (numbing medication) and want to discuss the options with your anesthesiologist
What Should Tell My Doctor?
Explain any allergies, including drug allergies you have. Let them know if you have anything that might interfere with imaging, such as metal objects in your body. Discuss past surgeries and procedures. Tell them about medications you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicine, herbs, vitamins, and supplements. Diagnostic tests may be recommended to help determine the cause of a thyroid disorder.
What Do I Need To Do?
You will be asked to sign a consent form that permits the procedure. Read the form carefully and ask questions if anything is not clear. Tell them about your past and current health history, including recent illnesses, accidents, or trauma. Let them know if you have had any anesthesia in the past and how long it has been since you had surgery or anesthesia. Also, inform the physician if you are pregnant or suspect that you may be pregnant. You can refuse treatment at any time during this process by saying “no” or refusing to sign the consent form.
How Is Ultrasonography Conducted?
The ultrasound is done in a doctor’s office or an outpatient center. If necessary, the doctor may do the test as an outpatient at a hospital or ambulatory clinic. The free-standing facility works for high-risk patients with difficult imaging studies or more complex procedures. The sonographer applies a conductive gel to the transducer and then presses it against your skin. You may feel pressure as they move it or discomfort when applying the gel, but the procedure is typically not painful for most people. Do not eat anything for four hours before having this test performed. Make sure you drink plenty of fluids before the test. Wear comfortable clothing for your exam. You may be asked to wear a gown.
The Different Types of Ultrasounds
Several types of thyroid-ultrasounds may be done based on your specific medical needs, including:
- Thyroid-sonogram – if your health care provider suspects you have a nodule or abnormal growth in the thyroid-gland. A sonogram can also help detect fluid around the thyroid-gland (cyst or goiter).
- Follicular imaging – sometimes done if you have hyperthyroidism.
- Thyroid-vascular imaging – helps the endocrinologist assess the vascular supply to the thyroid-gland. A thyroid-vascular ultrasound may check for abnormal blood flow in or near the thyroid-gland.
Who Will Help You Understand Thyroid-Ultrasound Results?
A radiologist interprets your thyroid-ultrasound. This is a doctor who specializes in giving and interpreting diagnostic imaging studies. They will send their written report to your physician or health care provider within 24 hours of completing the test.
Normal: The ultrasound shows a smooth, soft gland without any nodules, cysts, or asymmetry and normal vascular pattern and compressibility.
Unusual: The ultrasound reveals the gland’s nodules, cysts, or asymmetry and an abnormal vascular pattern.
How You Will Get Your Results
Your health care provider will contact you with your test results within 24 hours. If needed, you will be scheduled for further testing or additional procedures at that time. If you have a follow-up appointment with your healthcare provider, be sure to tell the staff that you had an ultrasound and when. Now that you understand ultrasonography and our services you can visit our facilities in Tampa, Florida for more information. We have many offices around this area for your convenience. Contact us. We will be more than happy to talk to you.