Ultrasound is a type of diagnostic imaging that uses high-frequency sound waves to produce an image of internal tissues. In medicine, ultrasound is used in many ways to perform various examinations and procedures. The most common use of ultrasound is imaging the fetus in utero to check for any congenital abnormalities. In medicine, ultrasound is also used to diagnose problems in internal tissues such as the thyroid. Here we will discuss thyroid ultrasonography and what it is used for by doctors.
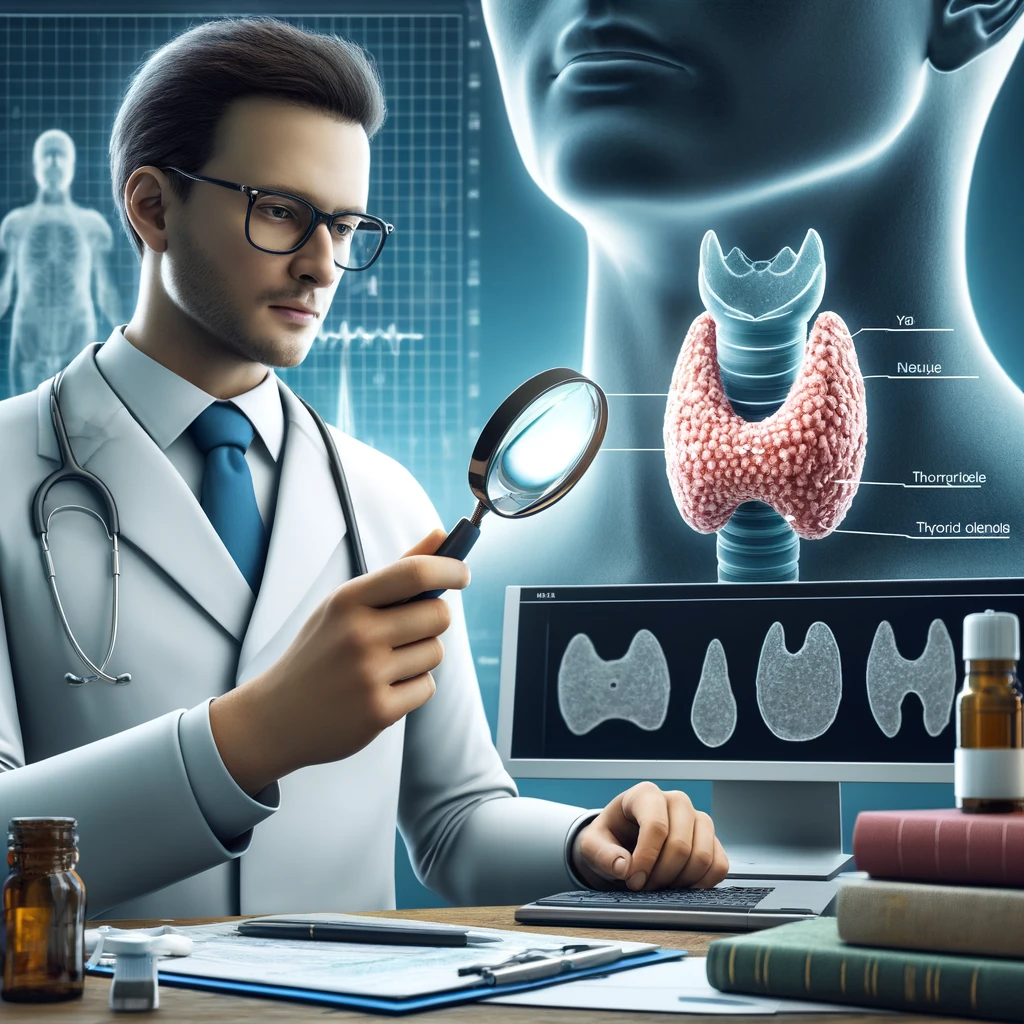
What is Thyroid
It is a small butterfly-shaped gland in the front lower part of the neck. It makes hormones that control how fast the body burns energy and how sensitive it should be to other hormones produced in other endocrine glands. The pituitary gland releases thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), which causes the gland to make these hormones.
The gland plays a critical role in regulating your metabolism. The two essential functions of the gland include the production of the hormone thyroxine and the promotion of iodine uptake by tissues. The hormones regulate metabolism and body temperature. In addition, they also help to control organs such as your heart, muscles, lungs, and brain.
The diseases that affect the gland are known as endocrine disorders. They affect the gland’s ability to produce hormones, causing many symptoms that vary depending on the disease. Symptoms of the diseases include weight gain in women, balding in men, and fatigue in children. But most often affect adults between 20 and 60 years of age.
What is Ultrasonography
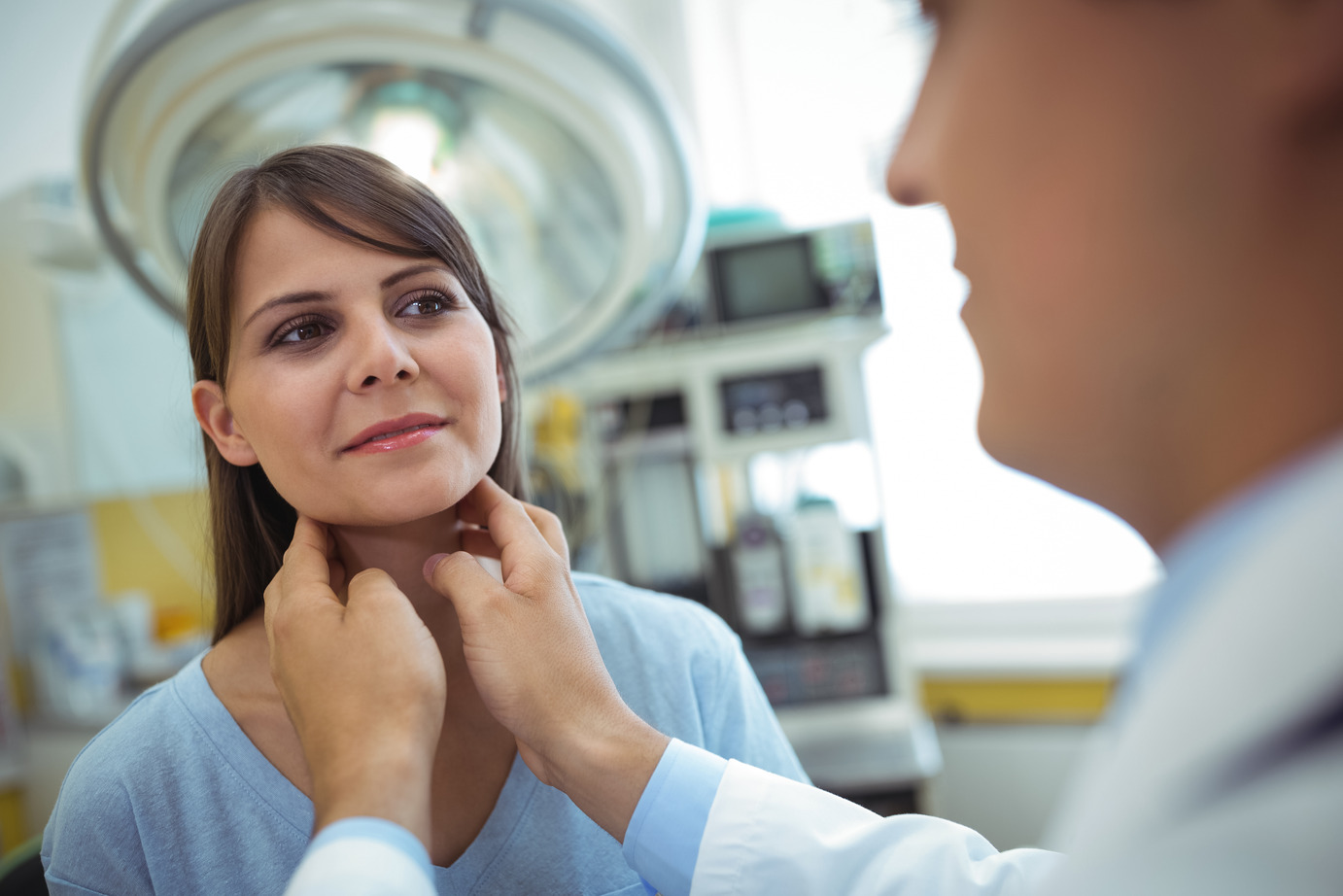
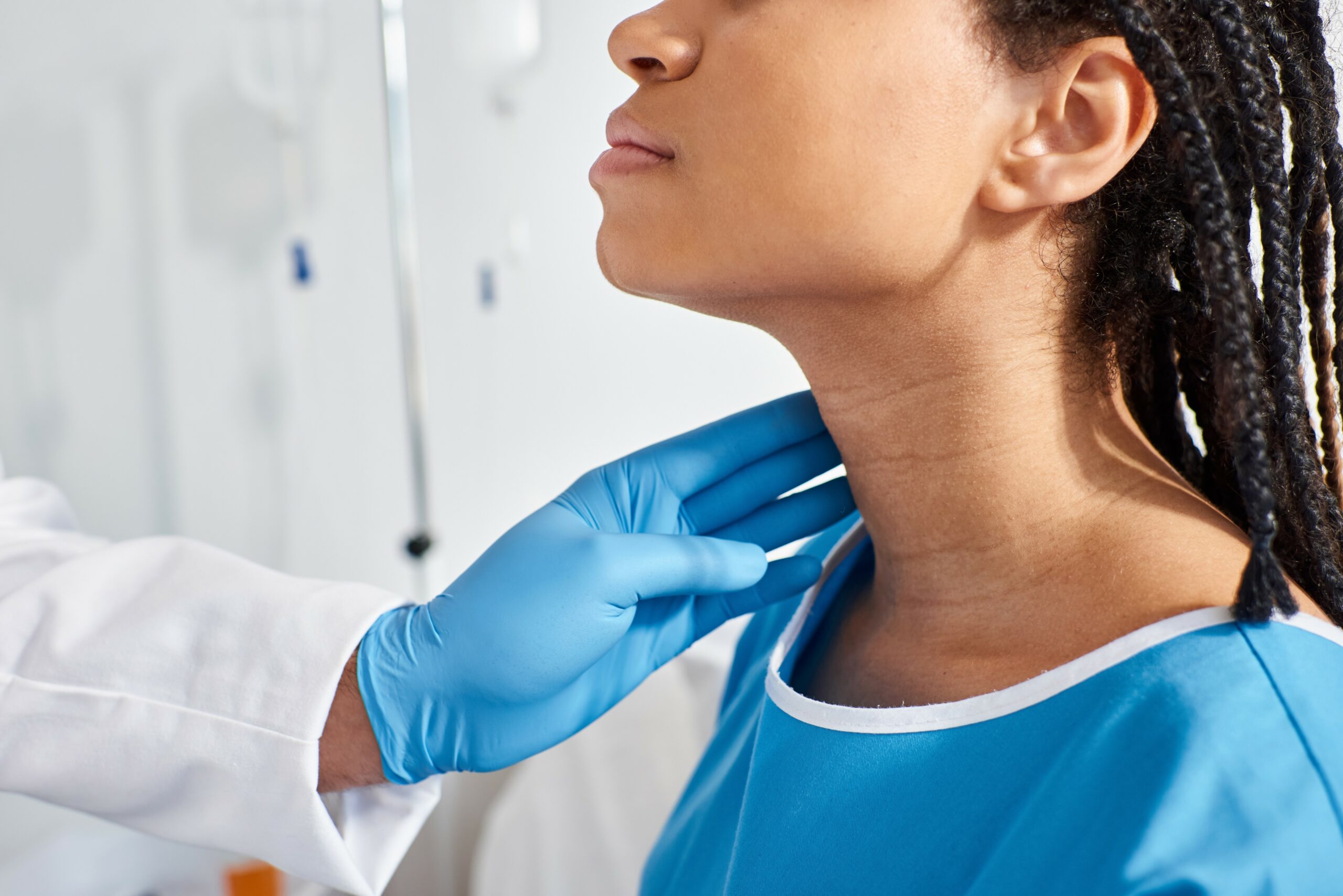
Ultrasonography is a noninvasive way to use high-frequency sound waves to produce an image of the inside of the body. In medicine, ultrasound machines are typically used to generate images of internal organs such as the thyroid and breasts.
The patient lies on a bed, and the ultrasound probe is placed on top of their organs. The search sends rapid pulses of sound waves at frequencies exceeding 20,000 cycles per second (Hz). When these sound waves hit the body’s internal tissue, they create recorded echoes.
These echoes are then electronically processed to produce images of the inside of the body. The images produced by ultrasound contain excellent detail and can be used to diagnose problems in internal tissues of the body. This technique is also more precise than X-rays because ultrasound pulses at a single frequency rather than rapid pulses at different frequencies.
Benefits
Ultrasonography helps to diagnose and detect some abnormalities of the gland. This examination is painless and can be performed anywhere, including in a patient’s home. It yields fast results that can quickly aid in the diagnosis process. Ultrasonography is also very accurate for identifying gland problems. The procedure does not expose the body to harmful ionizing radiation such as X-rays. This makes it a preferred method for many doctors to diagnose gland disease.
Common uses of Ultrasound
Everyday use of ultrasound is in detecting microcalcifications.Microcalcifications can increase the risk of developing certain cancers, including throat and breast cancer. Ultrasound examination allows doctors to see these calcifications early on before they can cause problems.
Screening for thyroid cancer. Cancerous cells in the gland often display abnormal features on ultrasound that are used to diagnose cancer. If an endocrinologist diagnoses it, the doctor treats it with surgery to remove the growth before it spreads.
Evaluation of hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism. One of the critical roles of ultrasonography is to screen patients for problems with their thyroids by providing a detailed view of their condition. When there is a problem with the gland, it can change in consistency or size. Ultrasound can detect these changes in the gland and alert the doctor to further testing to make a diagnosis.
Evaluation of nodules and goiters before thyroid surgery. A surgeon planning to perform surgery on a patient’s gland will use ultrasound before the procedure to determine if any problems exist with the gland. If the gland has a nodule, a cyst, or other abnormalities, it will be removed during surgery.
Testing the gland after radioactive iodine therapy. The ultrasound monitors patients who have undergone radioactive iodine treatment for hyperthyroidism and gland cancer. If the patient experiences any problems with their gland after treatment, an ultrasound is used to determine the problem and determine if further medical procedures are needed.
It is used to evaluate complications after thyroidectomy. Patients undergoing surgery to remove their gland may still have difficulties. Ultrasound can detect any problems with the gland after treatment, such as the presence of a cyst or any remaining nodules.
They are used in evaluating abnormal results on the gland blood tests. Although ultrasound is not a diagnostic test for the disease, it can confirm abnormal results from other blood tests, such as the thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) level.
Treatment
The gland is most often removed in cases of cancer. However, many other problems can cause a person to develop a nodule on their gland. Many times this growth is benign. This means that it is not cancerous and poses no danger to the patient.
If the patient has any concerns about the growth of their gland, they will undergo a series of tests to determine the type of condition they have. A lab test will be performed to determine if the growth is cancerous. If the patient has a cancerous gland, surgery will be recommended.
An endocrinologist who has detected thyroid cancer often recommends that the patient undergo radioactive iodine treatment, killing the gland’s cells. The gland then shrinks so it can no longer produce hormones.
Thyroid ultrasound is a noninvasive procedure used to detect abnormal growths or changes in the size of the gland. These changes often accompany disease in the gland and can cause many symptoms, such as weight gain, fatigue, and increased appetite. An endocrinologist often recommends that people undergo a ultrasound if they are experiencing these symptoms because it is a fast and reliable method for diagnosing disease. It is cost-effective and can be performed in a doctor’s office or the patient’s home.