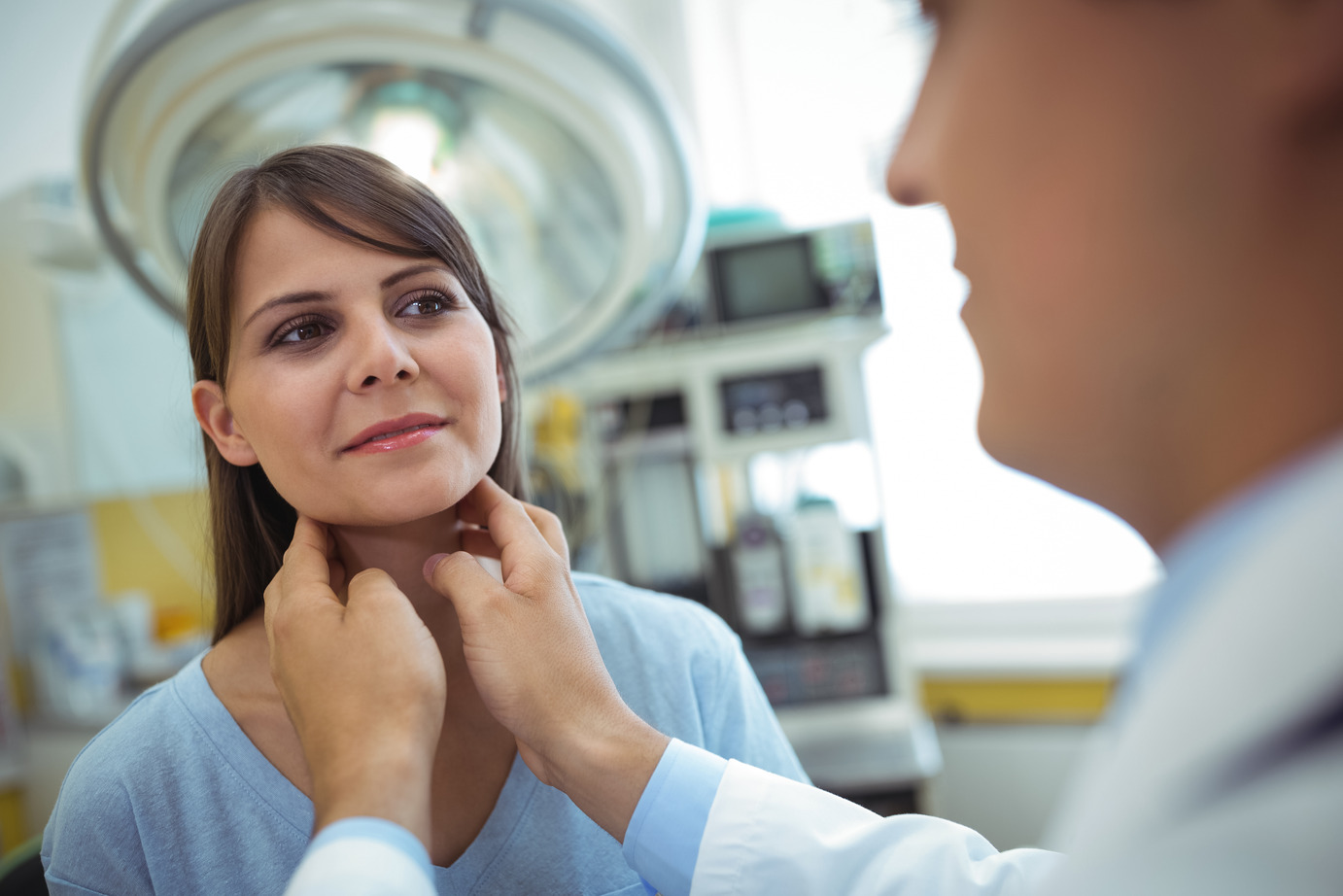
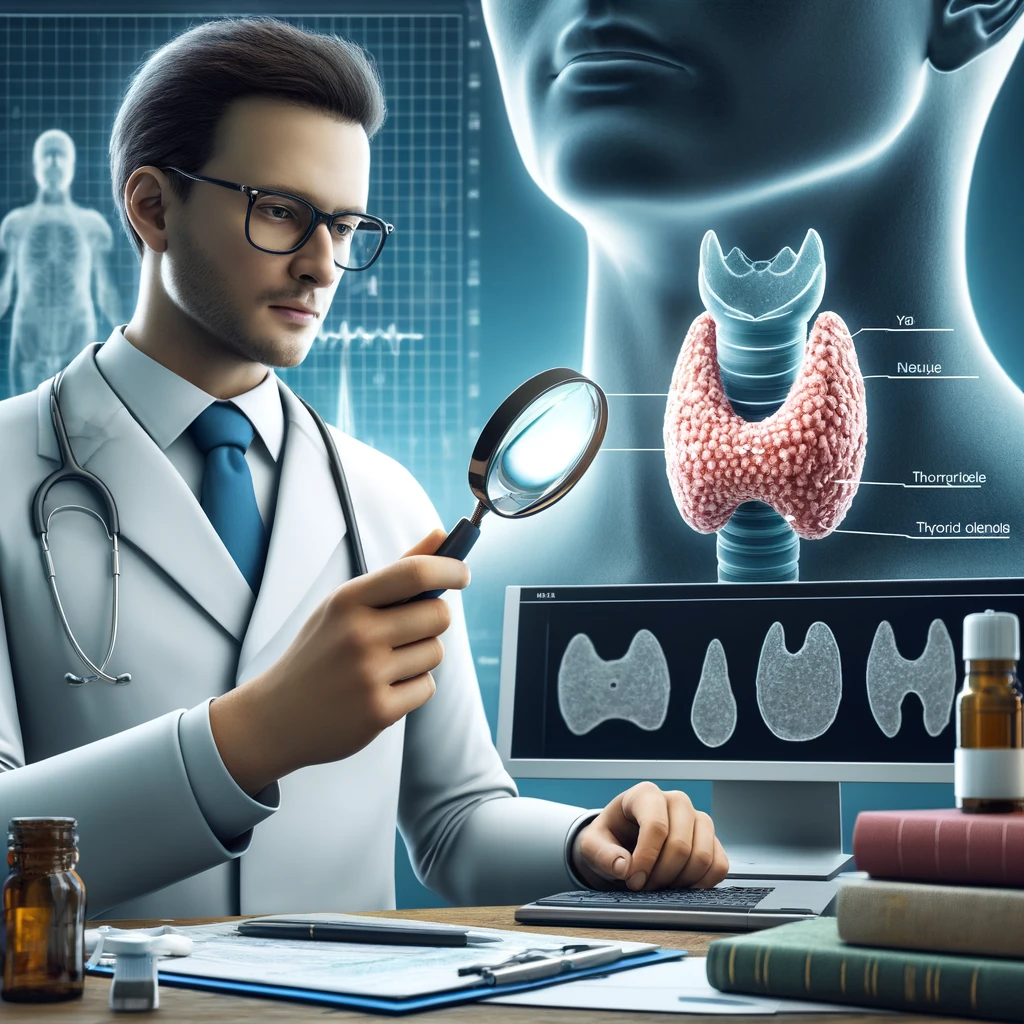
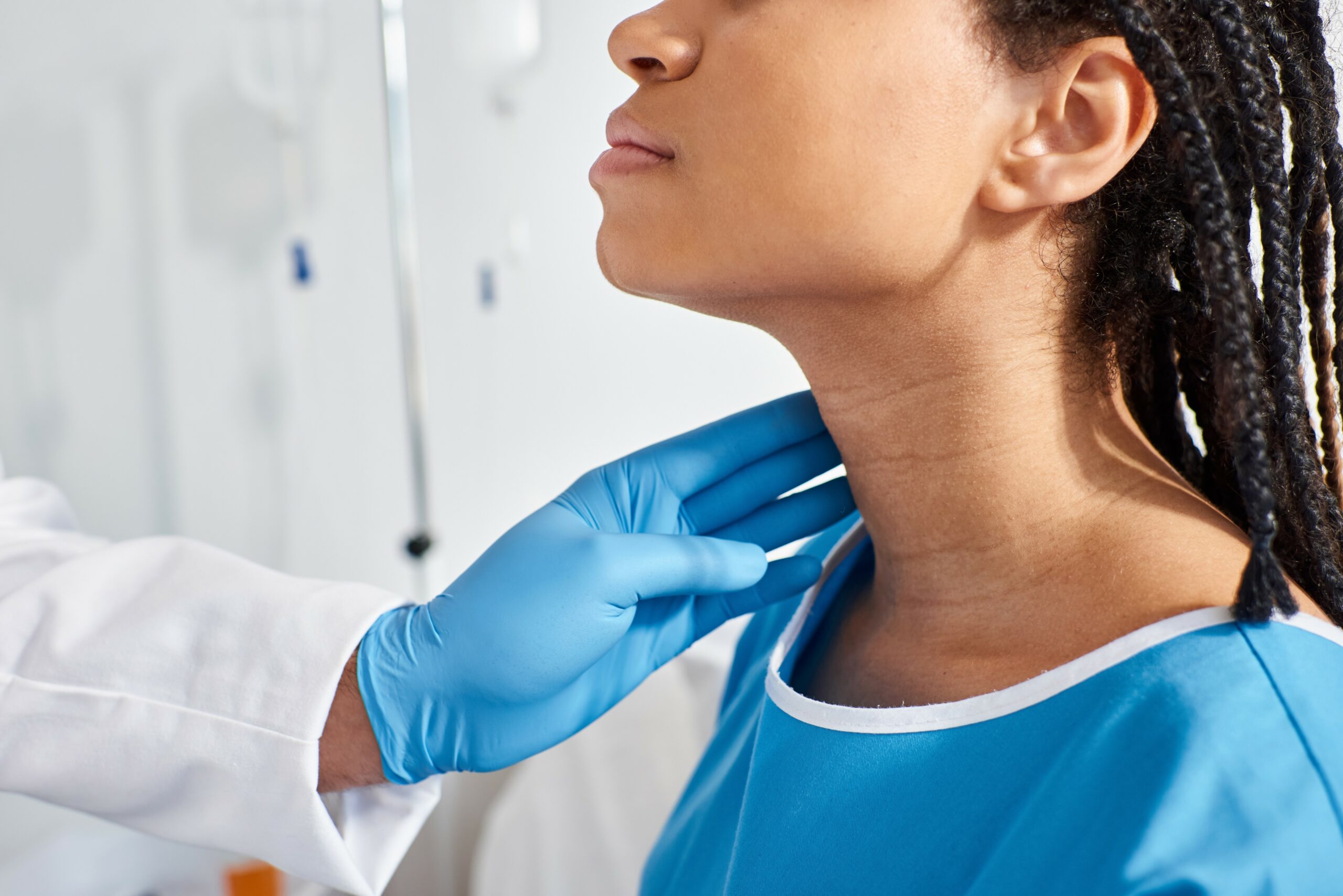
Multiple things must happen in the body to achieve homeostasis, the state of balance among all the body systems required for the body to survive and function optimally. And one of those things is a thyroid gland that secretes the right amount of two life-sustaining hormones, thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). If this butterfly-shaped gland secretes too much or too little of these hormones, it can spell trouble. Too much or too little T4 or T3 can trigger hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism. And both conditions will usually compel individuals to schedule an appointment with a licensed endocrinologist.
How Common Is Hyperthyroidism and Hypothyroidism?
Only 1% of the U.S. population suffers from hyperthyroidism. And only 5% suffer from hypothyroidism. So neither of these thyroid-related conditions are especially common in the U.S., but they can have a profound impact on those diagnosed with them. To put into perspective how these two thyroid-related conditions can affect someone’s life, it helps to look at some of the associated symptoms. The ones that go hand-in-hand with hyperthyroidism include the following: Chronic nervousness or irritability, fatigue, muscle weakness, heat intolerance, insomnia, tremors, arrhythmia, diarrhea, weight loss, mood swings, and developing a goiter or swollen neck, and difficulty breathing or swallowing.
As far as hypothyroidism is concerned, the most commonly reported symptoms to include the following: chronic fatigue, weight gain, a puffy face, cold intolerance, muscle, and joint pain, constipation, dry skin, thinning hair, anhidrosis, Heavy or irregular menstrual periods, fertility issues in women, depression, and bradycardia
Endocrinologists in Tampa Discuss Using Prescription Drugs to Treat Thyroid-Related Disorders
Thyroid hormone drugs can effectively treat hyperthyroidism. Some of the ones that physicians in Tampa, FL, including Dr. Pedro Troya, an endocrinology expert with Bay Area Endocrinology Associates in Tampa, Florida, prescribe the most include:
Methimazole (Tapazole) and propylthiouracil (PTU) – These particular drugs work by inhibiting the secretion of excessive amounts of t4 and t3 hormones. For this reason, they are among the go-to drugs for treating hyperthyroidism.
Radioactive iodine – Another go-to medication used to combat hyperthyroidism and the related symptoms is radioactive iodine. This medication works by destroying excessive t4 and t3 hormones and shrinking the overall size of an individual’s thyroid gland.
Beta-blockers – Although they are probably not the first drugs to come to mind for combating hyperthyroidism, they do work for that purpose, according to a study published by Cleveland Clinic. Along with being an excellent class of drugs for reducing high blood pressure, beta-blockers can help ease the tremors, rapid heartbeat, shakiness, and other symptoms associated with hyperthyroidism.
All of these treatment modalities to combat hyperthyroidism can sometimes cause side effects. Some of the ones commonly reported include developing a rash, itchy skin, unusual hair loss, and fever.
How Are Drugs Prescribed to Treat Hyperthyroidism Administered?
Methimazole, propylthiouracil, radioactive iodine, and beta-blockers are all taken orally, and they are generally safe when taken as prescribed by a physician. Studies show Methimazole and propylthiouracil, specifically, can reduce T4 and T3 hormone levels within 6 to 12 weeks. And most people also report experiencing relief from their hyperthyroidism symptoms. As far as radioactive iodine is concerned, most people will see a drop in their T4 and T3 levels within 1 to 3 months of being on the medication. Throughout that time, their struggles with hyperthyroidism symptoms will start to lessen. Beta-blockers work the fastest; studies show that individuals taking Propranolol and similar beta-blockers see a drop in T4 and T3 levels within minutes of administration, not to mention a noticeable easing of symptoms associated with hyperthyroidism.
Medications to Treat Hypothyroidism
Treating hypothyroidism typically entails using prescription-based drugs to replace T4 and T3 hormones that the body can no longer produce naturally. These hormone replacement drugs, available in tablet, capsule, and injectable form, might include Levoxyl, Synthroid, Tirosint, Unithroid, Unithroid Direct, and the generic levothyroxine. Studies show most individuals will see positive results in their hormone levels and experience relief from hypothyroidism symptoms within 6 to 8 weeks. That said, some unpleasant side effects can stem from taking levothyroxine and other hormone drugs, including unintended weight gain or weight loss, headache, vomiting and diarrhea, changes in appetite, and fever
All in all, thyroid-related disorders are rare, but they can be a nightmarish experience for those living with them. If you’re experiencing any of the symptoms detailed in this article, you’re encouraged to contact Bay Area Endocrinology Associates today.