813.876.3636
813.876.3636
FNA Molecular Testing is a biopsy of the cells collected by needle aspiration from the endocrine gland. This test allows doctors to determine the type of cells present in the endocrine gland. The molecular lab examines these cells under a microscope, uses statistical methodology to measure gene expression, and calculates the ratios of various proteins inside the cell. This process results in a list of gene mutations, copy number variations, or chromosomal abnormalities found in those cells. Dr. Pedro I. Troya, an experienced endocrinologist at Bay Area Endocrinology Associates, understands the importance of precise and timely diagnosis of endocrine gland conditions. With FNA Molecular Testing, he can provide patients with a comprehensive evaluation of their endocrine nodules, minimizing unnecessary surgeries and ensuring optimal treatment plans.
Thyroid nodules are benign growths of cells that form around the endocrine gland. They primarily develop in the tissues of the endocrine gland and can be found anywhere on the surface or deep within the tissue. Large numbers of nodules can crowd or compress neighboring structures, causing obstruction in significant structures such as the airway or esophagus. Nodules vary significantly in size, density, and appearance, but most are seen on ultrasound as solid without any fluid surrounding them.
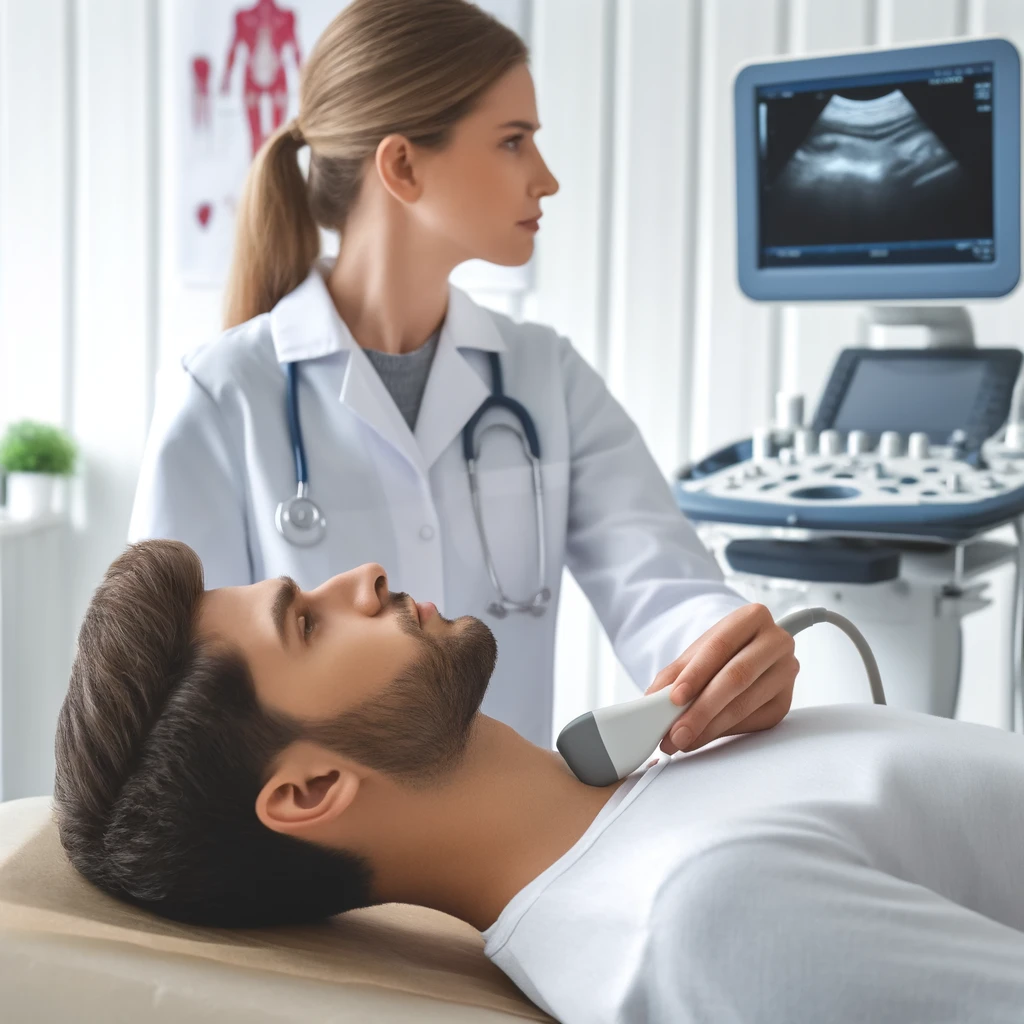
FNA Molecular Testing, also known as FNA cytogenetics, is an advanced diagnostic method for nodules in the endocrine gland. It involves collecting cells from an endocrine nodule through a fine needle aspiration (FNA) procedure. The cells are then evaluated in a lab for genetic mutations or alterations. Molecular testing focuses on specific genetic alterations associated with thyroid cancer. Typical markers include mutations in genes such as BRAF, RAS, and RET/PTC rearrangements. These markers help identify the presence of malignancy or predict the risk of malignancy in indeterminate nodules.
FNA Molecular Testing is a minimally invasive procedure in which a doctor uses ultrasound imaging to locate the nodule and guide the needle to the exact area. The needle is then inserted into the nodule to collect cells, which are sent to the molecular lab for analysis. Techniques such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and next-generation sequencing (NGS) are utilized to identify specific genetic alterations.
Interpreting the results of FNA molecular testing requires expertise and collaboration between pathologists, endocrinologists, and other healthcare professionals. A genetic alteration is considered positive if the gene expression from the malignancy marker exceeds that of adjacent or normal endocrine tissue. If a nonmalignant gene also has an elevated expression, it may be considered nonspecifically reactive. The gene must be compared to its standard counterpart to determine if the alteration is specific or nonspecific.
Traditional diagnostic methods like cytology and hormone assays provide a basic overview, often missing detailed genetic information. FNA Molecular Testing examines every cell for individual gene mutations, offering a more comprehensive and precise diagnosis. Traditional methods may identify the percentage of cells with mutations, but molecular testing provides a deeper genetic analysis.
This test is generally recommended for individuals with a suspicious lump or mass detected during a physical examination or imaging test. The FNA molecular test can help determine if the node is cancerous, guiding further treatment decisions. Discuss with your healthcare provider to determine the best timing for the test.
Nodules are usually asymptomatic, but some patients may experience symptoms such as:
Thyroid FNA Molecular Testing is a method to detect and diagnose thyroid cancer and other endocrine conditions. A doctor can perform a physical exam, imaging studies, and cytology tests to determine if you need testing, such as a biopsy or the FNA molecular test. This test can be performed safely on patients without anesthesia, sedation, or overnight hospital admissions. FNA Molecular Testing is a highly accurate and cost-effective method to detect endocrine nodules, diagnose malignancy, indeterminate nodules, or other endocrine conditions.
Our Endocrinologists, Dr. Carlo A. Fumero, Sean Amirzadeh, DO, Alberto Garcia Mendez, Lauren Sosdorf, and Pedro Troya, are board certified by the American Board of Internal Medicine and have a wealth of experience treating thyroid conditions. They will work with you to create a personalized treatment plan that meets your unique needs.





Tampa Office:
Zephyrhills Office:
Plant City Office: